Impala Data Cache Testing
- 1. Introduction to the test environment
- 2. Basic Concept
- 3. List Data cache files
- 4. Run Demo Queries
- 5. Conclusion
1. Introduction to the test environment
| CDP Runtime version | CDP PvC Base 7.1.7 SP2 |
| CM version | Cloudera Manager 7.10.1 |
| ECS version | CDP PvC DataServices 1.5.1 |
| OS version | Centos 7.9 |
| K8S version | RKE 1.24 |
| Whether to enable Kerberos | Yes |
| Whether to enable TLS | Yes |
| Auto-TLS | Yes |
| Kerberos | FreeIPA |
| LDAP | FreeIPA |
| DB Configuration | External Postgres 12 |
| Vault | Embedded |
| Docker registry | Embedded |
| Install Method | Internet |
2. Basic Concept
When Impala compute nodes and its storage are not co-located, the network bandwidth requirement goes up as the network traffic includes the data fetch as well as the shuffling exchange traffic of intermediate results. To mitigate the pressure on the network, you can enable the compute nodes to cache the working set read from remote filesystems, such as, remote HDFS data node, S3, ABFS, ADLS.
- To enable remote data cache, set the –data_cache Impala Daemon start-up flag as below:
--data_cache=dir1,dir2,dir3,...:quota- The flag is set to a list of directories, separated by ,, followed by a :, and a capacity quota per directory.
- Cached data is stored in the specified directories. The specified directories must exist in the local filesystem of each Impala Daemon, or Impala will fail to start.
- The cache can consume up to the quota bytes for each of the directories specified.
- You configure a cache eviction policy using the –data_cache_eviction_policy Impala Daemon start-up flag:
--data_cache_eviction_policy=policy.- In Impala 3.4 and higher, you can configure one of the following cache eviction policies for the data cache:
- LRU (Least Recently Used – the default)
- LIRS (Inter-referenece Recency Set)
- Please see details about Data Cache for Remote Reads.
- In Impala 3.4 and higher, you can configure one of the following cache eviction policies for the data cache:
3. List Data cache files
- Get all start-up flagfile in CDW impala.
- The target configmap is
impala-executor-000-flagfile.
- The target configmap is
$ kubectl get configmap -n impala-impala01|grep flagfile
impala-autoscaler-flagfile 1 47h
impala-catalog-flagfile 3 47h
impala-coordinator-flagfile 5 47h
impala-executor-000-flagfile 3 47h
impala-statestore-flagfile 2 47h
- Get data cache settings in Impala Daemon start-up flag.
- The target data cache directory is
/opt/impala/cacheand it’s quota is48GB. - The cache eviction policy is
LRU.
- The target data cache directory is
$ kubectl describe configmap impala-executor-000-flagfile -n impala-impala01 |grep data_cache
--data_cache=/opt/impala/cache:48GB
--data_cache_eviction_policy=LRU
- Get data cache volume name in impala executor definition.
- The target volume is
scratch-cache-volume.
- The target volume is
$ kubectl describe pod impala-executor-000-0 -n impala-impala01|grep /opt/impala/cache
/opt/impala/cache from scratch-cache-volume (rw)
- Get pvc name in impala executor definition.
- The target pvc is
scratch-cache-volume-impala-executor-000-0.
- The target pvc is
$ kubectl describe pod impala-executor-000-0 -n impala-impala01|grep -A3 scratch-cache-volume:
scratch-cache-volume:
Type: PersistentVolumeClaim (a reference to a PersistentVolumeClaim in the same namespace)
ClaimName: scratch-cache-volume-impala-executor-000-0
ReadOnly: false
- Get the target pv name which is
pvc-f9a4403c-caad-4d8e-aa6f-dc4ca496d3e8.
$ kubectl get pv|grep scratch-cache-volume-impala-executor-000-0
pvc-f9a4403c-caad-4d8e-aa6f-dc4ca496d3e8 94Gi RWO Delete Bound impala-impala01/scratch-cache-volume-impala-executor-000-0 local-path 47h
- Get the host and the local storage path.
- The target host is
feng-ws4.sme-feng.athens.cloudera.com - The target path is
/mnt/ecs/local-storage/pvc-f9a4403c-caad-4d8e-aa6f-dc4ca496d3e8_impala-impala01_scratch-cache-volume-impala-executor-000-0and it’s max capacity is94GB.
- The target host is
$ kubectl describe pv pvc-f9a4403c-caad-4d8e-aa6f-dc4ca496d3e8
Capacity: 94Gi
Node Affinity:
Required Terms:
Term 0: kubernetes.io/hostname in [feng-ws4.sme-feng.athens.cloudera.com]
Message:
Source:
Type: HostPath (bare host directory volume)
Path: /mnt/ecs/local-storage/pvc-f9a4403c-caad-4d8e-aa6f-dc4ca496d3e8_impala-impala01_scratch-cache-volume-impala-executor-000-0
HostPathType: DirectoryOrCreate
Events: <none>
- Open SSH terminal for the host
feng-ws4.sme-feng.athens.cloudera.comand list the cache files.- data_cache:
impala-cache-file-f0464322167cea8e:7c5b604bc879efb7to cache the working set read from remote HDFS data node - srcatch_dirs:
impala-scratchto store intermediate files
- data_cache:
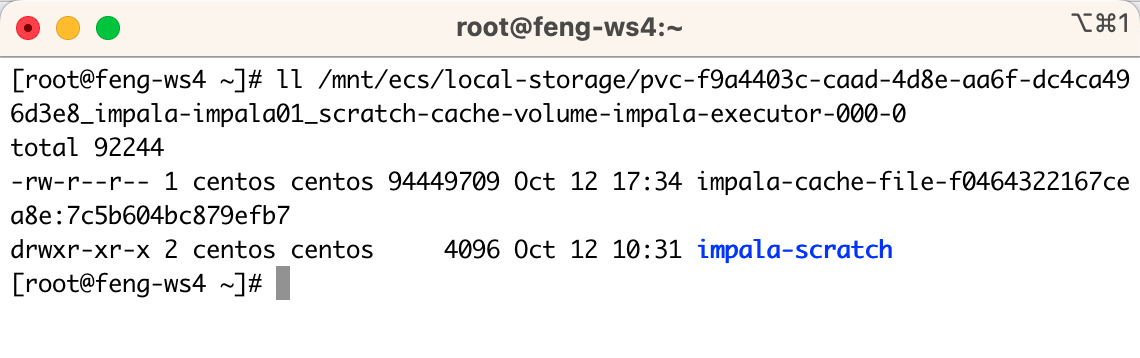
[root@feng-ws4 ~]# ll /mnt/ecs/local-storage/pvc-f9a4403c-caad-4d8e-aa6f-dc4ca496d3e8_impala-impala01_scratch-cache-volume-impala-executor-000-0
total 92244
-rw-r--r-- 1 centos centos 94449709 Oct 12 17:34 impala-cache-file-f0464322167cea8e:7c5b604bc879efb7
drwxr-xr-x 2 centos centos 4096 Oct 12 10:31 impala-scratch

4. Run Demo Queries
- On the Overview page under Virtual Warehouses, click the options menu in the upper right corner of an Impala Virtual Warehouse tile, and select
SQL Editor.
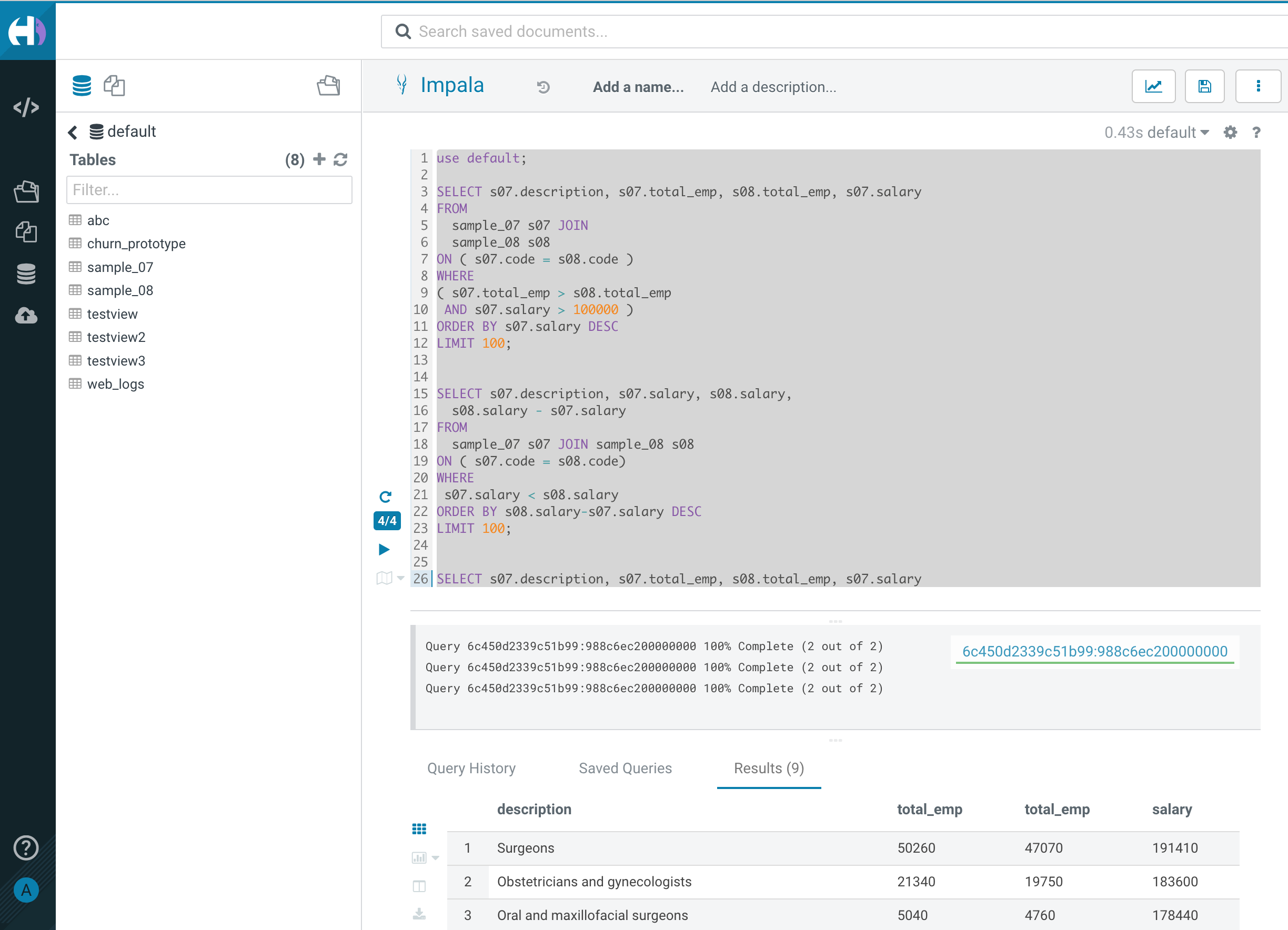
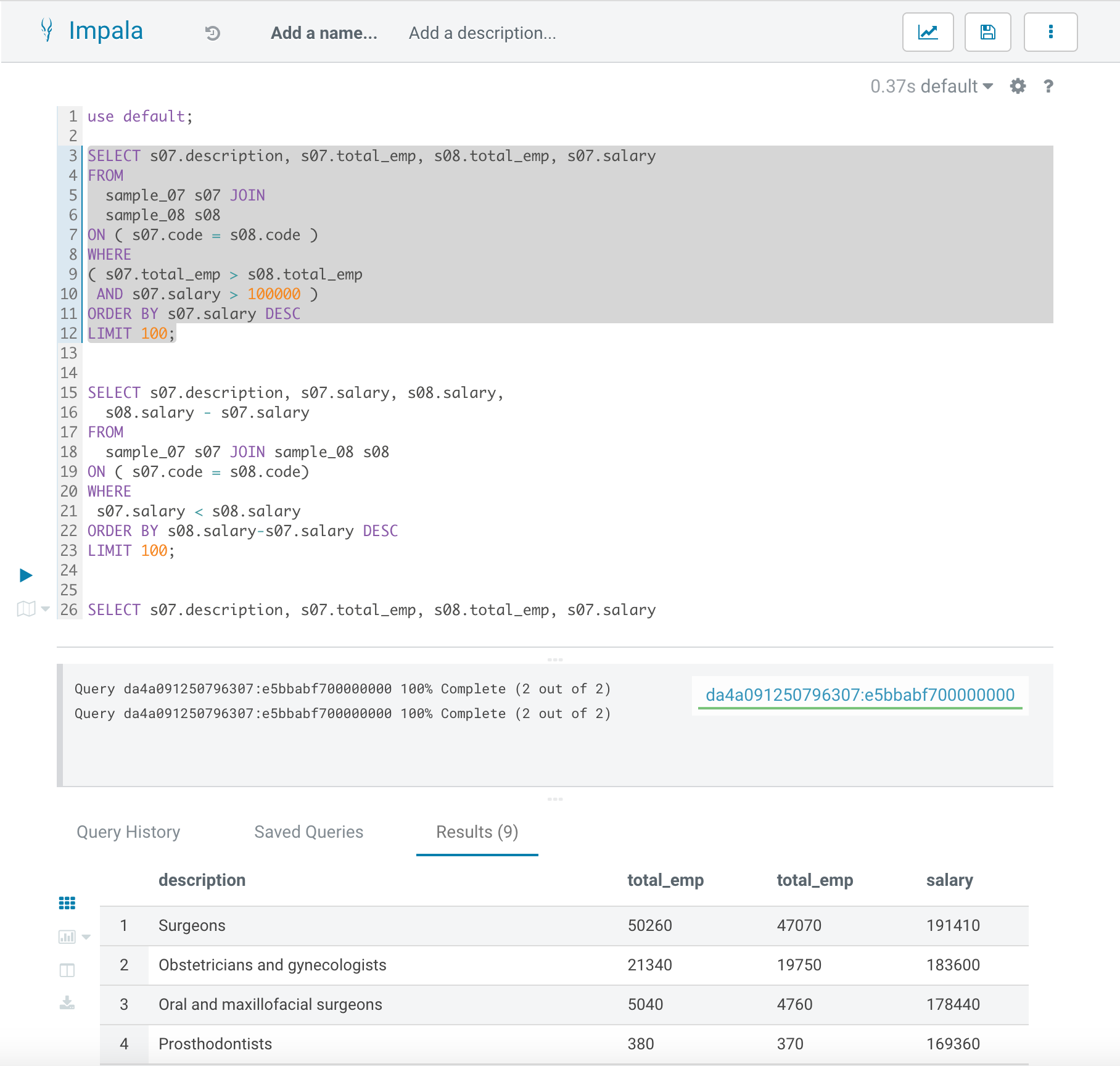
- Submit Impala queries as followings with Hue.
use default;
SELECT s07.description, s07.total_emp, s08.total_emp, s07.salary
FROM
sample_07 s07 JOIN
sample_08 s08
ON ( s07.code = s08.code )
WHERE
( s07.total_emp > s08.total_emp
AND s07.salary > 100000 )
ORDER BY s07.salary DESC
LIMIT 100;
SELECT s07.description, s07.salary, s08.salary,
s08.salary - s07.salary
FROM
sample_07 s07 JOIN sample_08 s08
ON ( s07.code = s08.code)
WHERE
s07.salary < s08.salary
ORDER BY s08.salary-s07.salary DESC
LIMIT 100;
SELECT s07.description, s07.total_emp, s08.total_emp, s07.salary
FROM
sample_07 s07 JOIN
sample_08 s08
ON ( s07.code = s08.code )
WHERE
( s07.total_emp > s08.total_emp
AND s07.salary > 100000 )
ORDER BY s07.salary DESC
LIMIT 100;
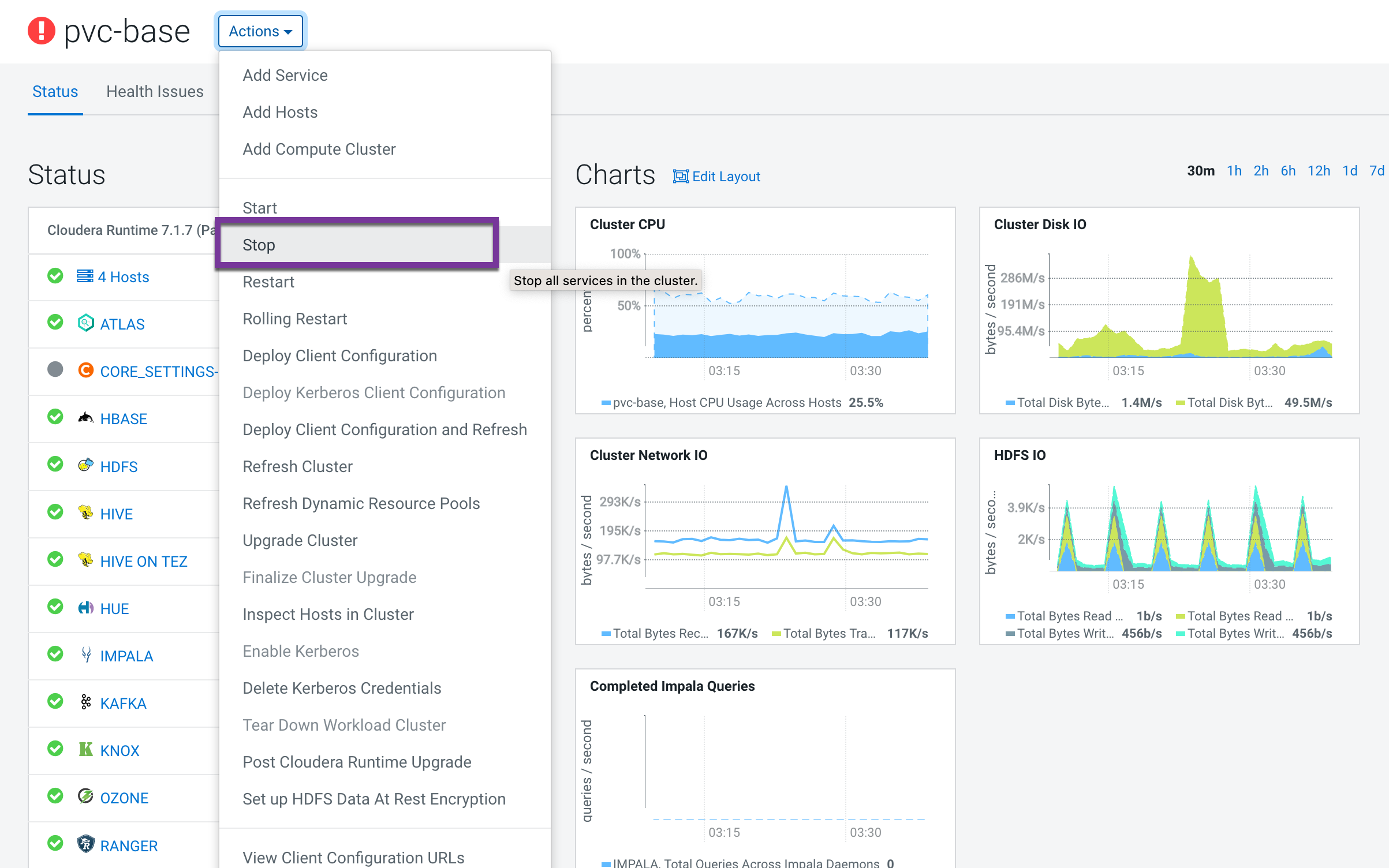
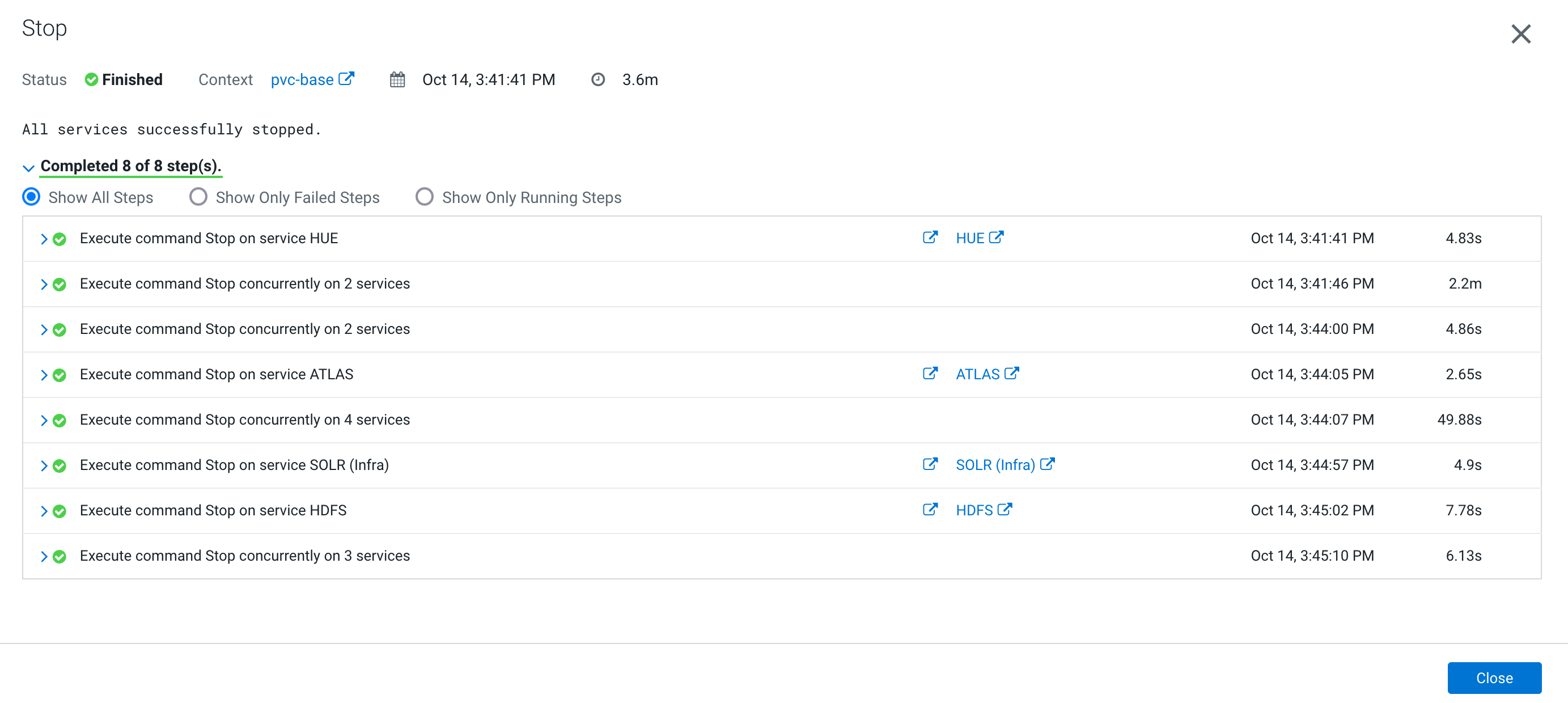
- Stop CDP Base Cluster.
- The previous queries still run normally. This is true even if the Base cluster has been stopped for more than 1 day.
- The cache item won’t expire as long as the same file metadata is used in the query. The reason is that the cache key is (filename, mtime, file offset) where mtime is the last modified time of the file. When the mtime in the file metadata doesn’t change, the scan request could always hit the cache (if capacity is enough). Please see IMPALA-12491.
- New query gets stuck, even if the query is very simple.
- Let’s check the local path again, nothing has changed.
5. Conclusion
- Impala Data Cache saves the data files from the remote storage layer in local storage on the node on which the impala daemon is running. Subsequent queries that require the same data or a subset thereof will not require IO from the remote storage layer to access the data.
- The default evict policy is LRU (Least Recently Used), if no new query writes any more result sets into the data cache(i.e. the scenario when CDP Base Cluster is down), the data cache will never exceed the max capacity, so the scan request of old queries could always hit the cache.